‘Forever Chemicals’ Found in Every Umbilical Cord Blood Sample in Global Study
(Photo: Alexander Grey/Unsplash)“Forever chemicals,” or perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), have made quite a few appearances in the news cycle lately. These thousands of manufacturing chemicals leach into the food and water supply, making it nearly impossible to avoid absorption into the human body. Once in the body, they don’t go away—hence the name “forever chemicals”—and can cause a host of health concerns, from thyroid disease and cancer to liver damage and fertility issues.
Unfortunately, it now appears we might have yet another reason to worry about PFAS prevalence. A global study examining more than 30,000 umbilical cord blood samples recently found PFAS in every single one. Worse, these samples were up to five years old—meaning PFAS have been nearly ubiquitous for longer than we otherwise might have thought.
The study was conducted by the Environmental Working Group (EWG), an environmental and public health nonprofit. EWG scientists reviewed 40 studies on the presence of PFAS in umbilical cord blood from citizens of the US and 11 other countries, including China, Japan, and Brazil. All of them reported a range of PFAS were found in their respective samples, with 14 studies in particular linking PFAS presence in the umbilical cord with PFAS detection later in childhood, as well as increased health risks in adulthood.
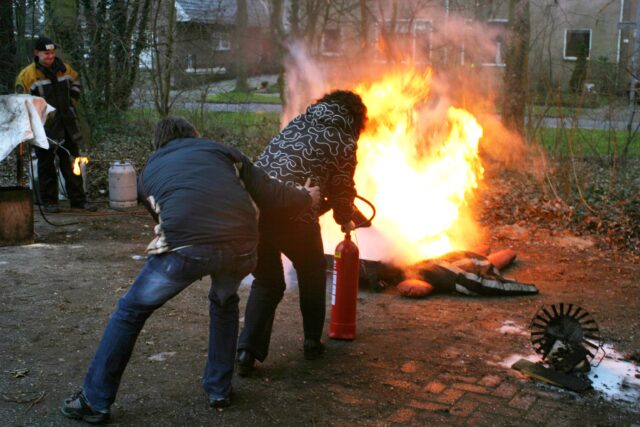

PFAS are commonly used in the manufacturing of firefighting foams. (Photo: Andries Meijer/Unsplash)
Developing fetuses are particularly vulnerable to PFAS because they “don’t have the mechanisms to deal with the chemicals,” EWG researcher Uloma Uche told The Guardian. “Even before you’ve come into the world, you’re already exposed to PFAS.”
That PFAS were detected in umbilical cord blood is altogether unsurprising, given the chemicals’ pervasiveness in US adults. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has previously reported that most Americans have one of two common PFAS in their blood: perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA). Like many other PFAS, both of these are used to make firefighting foams and water- or oil-resistant materials. Though PFOS and PFOA usage are declining, the CDC warns they might very well be replaced with other, equally-harmful PFAS.
Not all hope is lost. Two separate studies found ways to eliminate PFAS this year alone, one using ultraviolet light and common kitchen ingredients while the other used lye and a chemical solvent. Both methods have their caveats (the first requires a fair bit of scaling up to be effective, while the other only works on some PFAS), but together, they represent a potential pivot in our collective level of risk in the face of pervasive chemical compounds.
Now Read:

Comments are closed.